What to Expect After an Abortion: A Practical Guide to Physical and Emotional Recovery
An abortion – whether medication-based or surgical – sets off a series of physical and emotional changes as your body settles back toward its pre-pregnancy state. This guide walks through common physical symptoms (bleeding, cramping, discharge, breast changes), the hormonal shifts involved (hCG, estrogen, progesterone), and typical emotional responses so you know what’s normal and when to get care. People often want clear timelines, practical self-care steps, and reassurance about fertility and future family planning; this article delivers those answers in plain, evidence-informed language. You’ll find a recovery timeline, symptom-by-symptom explanations, pain and bleeding management tips, warning signs to watch for, and contraception planning. Each section includes actionable checklists and simple comparisons to help you follow your recovery during the hours, days, and weeks after the procedure. Read on to learn common recovery patterns, how hormones affect what you feel, and where to find support if you need it.
Follow Us!
How long does the abortion recovery timeline last?
“Recovery” refers to the time your body takes to expel pregnancy tissue, shrink the uterus back to its usual size, and for hormone levels and symptoms like bleeding and cramping to settle. How long that takes depends on the type of procedure (medical versus surgical), how far along the pregnancy was, and individual health differences. For some people, the most intense symptoms last a few hours or days; for others, light spotting or intermittent symptoms continue for several weeks. Early milestones commonly include heavier bleeding and stronger cramping in the first 4–6 hours (and sometimes up to 24–72 hours), with a gradual taper in bleeding and pain over the next 1–2 weeks for many people. Knowing these stages can help you plan rest, work, and follow-up care — and reduce worry about what’s normal.
Quick snapshot: the table below summarizes typical symptom durations for medical versus surgical abortion so you can compare what to expect in the early recovery phase.
| Symptom | Typical Duration (Medical Abortion) | Typical Duration (Surgical Abortion) |
|---|---|---|
| Heavy bleeding/cramping (intense) | 4–24 hours, up to 72 hours in some | 12–48 hours |
| Ongoing lighter bleeding/spotting | Up to 2–4 weeks | 1–2 weeks |
| Severe cramping requiring stronger pain relief | First 1–3 days | First 24–48 hours |
| When to expect follow-up confirmation | 1–2 weeks (may require hCG or clinic confirmation) | Often within 1–2 weeks or at clinician’s schedule |
This comparison shows that medical abortions often involve longer spotting as medication causes the body to pass tissue over time, while surgical procedures usually lead to a shorter, more immediate recovery period. If you’d like personalized follow-up or extra reassurance about your recovery, Her Smart Choice offers compassionate information and support tailored to post-abortion needs to help you decide on clinical follow-up or self-care steps.
What is the typical duration of physical recovery after abortion?
Physical recovery generally follows a familiar pattern: the first hours and days are the most intense, then symptoms ease over days and weeks as hormones and uterine size return toward baseline. Most people have the heaviest bleeding and strongest cramping within the first 4–24 hours, with noticeable improvement by the end of week one. Light bleeding or spotting may continue intermittently for up to 2–4 weeks for many. Systemic symptoms such as tiredness or mild nausea usually resolve within a few days. Knowing this typical arc helps you plan pain control, rest, and a safe return to daily activities while recognizing when to seek medical help.
How does recovery differ between medical and surgical abortions?
Medical abortion uses medication to trigger uterine contractions and tissue passage, so bleeding and cramping can be intense but often occur over several hours to days, with spotting that may continue for a few weeks. Surgical abortion usually produces a shorter recovery: bleeding and cramps are often worst immediately after the procedure and then decline more quickly over the next days. Follow-up also differs: medical abortion may need a clinic visit or hCG check to confirm completion, while surgical abortion often includes immediate clinical confirmation. These differences influence choices about pain control, timing for returning to work, and scheduling contraception or follow-up visits.
What are the common physical changes after an abortion?

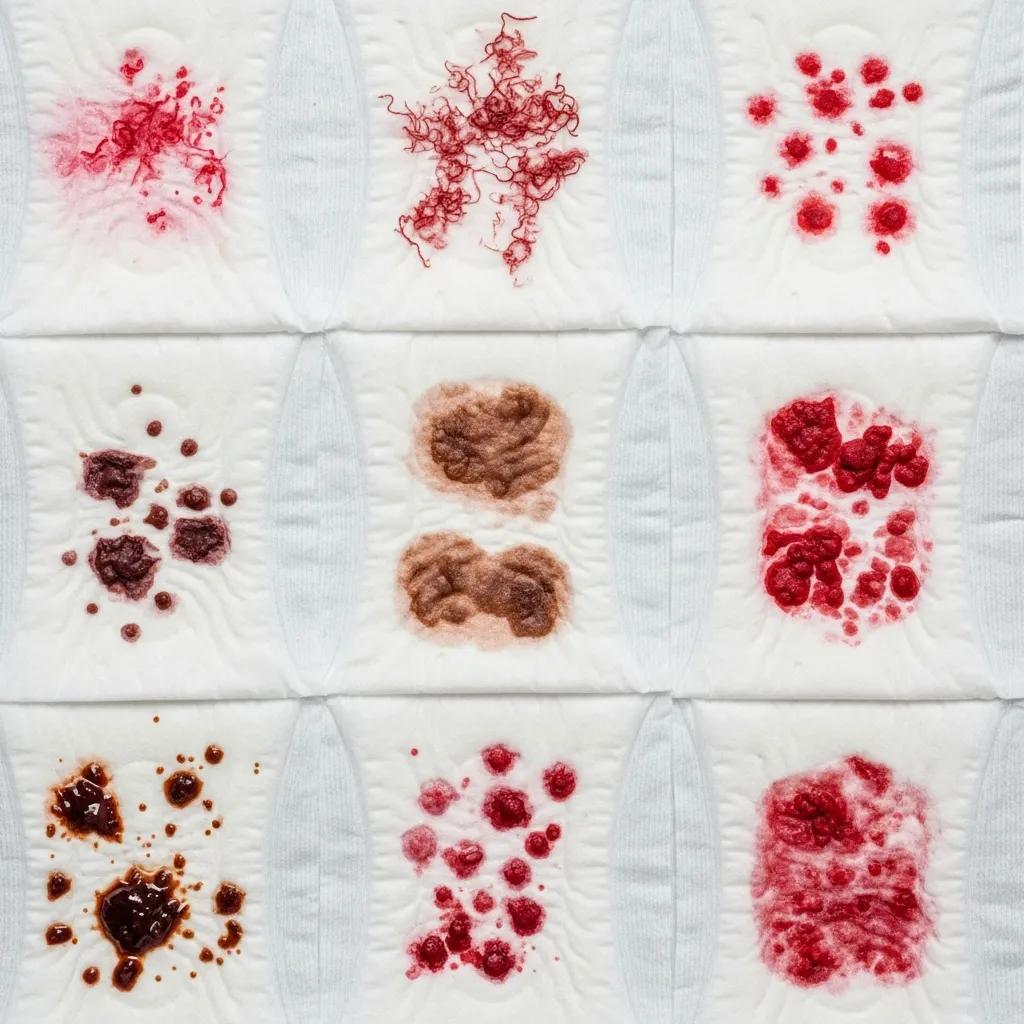
Many physical signs after an abortion are expected and reflect the body’s hormonal and physical adjustments as pregnancy tissue resolves and the uterus contracts back to its usual size. Typical changes include bleeding that can range from heavy flow to light spotting, uterine cramping, vaginal discharge as tissues heal, and breast tenderness as pregnancy hormones fall. You may also feel tired, slightly nauseated, dizzy, or notice temporary changes in appetite or sleep — these usually improve over days to a few weeks. Additional insights can be found in hormonal shifts after abortion.
Below is a practical chart linking common symptoms with likely causes and simple self-care steps to manage each during recovery.
| Symptom | Cause / Mechanism | Suggested Self-Care |
|---|---|---|
| Bleeding (heavy to spotting) | Uterine shedding of pregnancy tissue and hormonal withdrawal | Use pads, rest during heavy flow, avoid tampons for advised period, monitor volume |
| Cramping | Uterine contractions to expel tissue and shrink the uterus | OTC pain relief, heat packs, paced rest, light movement as tolerated |
| Vaginal discharge | Healing of cervix and endometrial shedding | Maintain hygiene, avoid baths or douching for advised period, watch for foul odor |
| Breast tenderness | Sudden drop in pregnancy hormones (estrogen/progesterone) | Supportive bra, warm/cool compresses, expect gradual resolution |
This table explains why symptoms occur and simple home steps that often help. If you notice unusual signs like a foul odor, fever, or rapidly worsening pain, contact a clinician promptly.
What post-abortion symptoms should you expect?
You can expect a variety of symptoms that differ in intensity between people; the most common are bleeding, cramping, breast tenderness, and short-term systemic effects such as fatigue. Bleeding may be heavy with clots the first day or two, then taper to light spotting over weeks. Cramping is often like menstrual cramps but can be stronger at first. Breast tenderness comes from the sudden hormone drop and usually eases over days to a few weeks. Tracking timing and intensity helps you tell normal recovery from signs that need medical attention.
How do hormonal shifts affect your body after an abortion?
After an abortion the body moves quickly through hormonal changes as pregnancy hormones fall and the menstrual cycle begins to reset. The most obvious shift is the drop in hCG as pregnancy tissue passes, followed by declines in estrogen and progesterone. Those decreases cause uterine bleeding, cramping, breast changes, and mood or energy shifts. Most hormone-related symptoms ease over several weeks as levels stabilize and your next period approaches. Understanding this process explains why some symptoms feel sudden at first and then gradually settle.
Ovarian Hormonal Stress Following Medical Abortion: A Study of Hormonal Status Abortion means ending a pregnancy, and that change brings measurable shifts in the body’s hormones. Early medical abortion — which uses medications to end a pregnancy — is generally seen as a conservative method, but the body does experience physiological stress as it stops preparing for gestation and lactation. Research on pituitary and ovarian changes after medical abortion is limited, which motivated our investigation. In this study we observed 50 women without contraindications to describe post-abortion hormonal status and related changes. OVARIAN HORMONAL STRESS AFTER MEDICAL ABORTION, NA Abenova, 2022
Which hormones change and what are their effects?
Human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) falls quickly after pregnancy tissue leaves the body, signaling the end of pregnancy and triggering downstream hormonal adjustments. Estrogen and progesterone then decline, which reduces support for the uterine lining and causes bleeding and cramping; those drops also explain breast tenderness and shifts in mood or energy. Over several weeks hormone levels usually move back toward baseline, letting the hypothalamic-pituitary-ovarian axis reestablish regular cycles. Knowing which hormones shift helps explain why some physical and emotional reactions are strongest early in recovery and why the return of the menstrual cycle varies.
How does breast tenderness manifest post-abortion?
Breast tenderness is common after an abortion because pregnancy hormones that prepared the breasts for lactation drop rapidly, and the breast tissue adjusts back toward its pre-pregnancy state. Sensations can range from mild soreness to fullness, and occasional leaking is possible but uncommon. Symptoms usually improve over days and resolve in a few weeks. Practical steps include wearing a supportive bra, using warm or cool compresses for comfort, and avoiding breast stimulation if you don’t want to provoke milk production. Seek care if you develop severe swelling, fever, or abnormal nipple discharge.
What emotional effects can occur after an abortion?

Emotional reactions after an abortion are varied and normal: people commonly feel relief, sadness, grief, guilt, anxiety, or a mix of responses as hormones change and they process the experience. The timing and intensity of feelings differ widely and depend on mental health before the procedure, available support, personal values, and the circumstances that led to the decision. Many people find emotions fluctuate over days to weeks and lessen over time with supportive conversations and self-care. Remember that there’s no single “right” response — and it’s okay to seek help if feelings are interfering with day-to-day life.
Psychological Coping During the Immediate Post-Abortion Period The time from the abortion procedure until bleeding stops is a period of both physical and emotional adjustment. During this phase, individuals may experience symptoms such as cramping, bleeding, and breast tenderness alongside emotions like relief, sadness, or worry. Giving accurate information and strong support during this immediate period helps people recover more smoothly. Psychological coping in the immediate post-abortion period, SJ Ratcliffe, 2014
What are the common emotional responses after abortion?
Common emotional responses include relief at ending an unwanted pregnancy, sadness or grief over the loss of a potential pregnancy, guilt or shame if cultural pressures are present, and anxiety about physical recovery or future fertility. These feelings often come in waves and may be triggered by reminders like seeing a baby or attending follow-up visits — and it’s normal to feel several things at once (for example, relief and sadness). Research shows people’s experiences vary; some have brief emotional upset while others find counseling helpful. Naming and acknowledging your feelings is a helpful first step toward coping and planning support.
How can you heal emotionally and cope with post-abortion feelings?
Emotional healing usually combines practical self-care, supportive people, and professional help if needed. Options that help include talking with trusted friends or a counselor, practicing grounding or mindfulness, journaling, and engaging in restorative activities. Peer support or structured counseling can reduce distress for many people. Partners and support people can be helpful by listening without judgment, helping with daily needs during recovery, and encouraging professional care when feelings feel overwhelming. If you have persistent depression, severe anxiety, or thoughts of self-harm, seek mental health support right away.
How can you manage post-abortion symptoms and care for your body?
Managing symptoms focuses on safe pain relief, controlling bleeding, preventing infection, and gradually returning to normal activities. At-home strategies that often help include using recommended over-the-counter pain medicines, applying heat to ease cramps, resting during heavy bleeding, and following hygiene guidance to lower infection risk. Slowly reintroduce exercise and work to avoid setbacks, and make a follow-up plan with a clinician or support service so any concerns can be addressed quickly. Clear guidance on tampon use, sexual activity, and wound care helps protect healing during the first weeks. For further reading, you can visit how long do you bleed after an abortion.
What are effective pain management and bleeding control methods?
Start with over-the-counter nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) taken as directed to reduce cramping and inflammation; combine this with heat therapy and rest for extra relief. For bleeding, use pads rather than tampons for the recommended period to minimize infection risk, and keep an eye on volume and clot size to detect heavy bleeding. Non-medication approaches like staying hydrated, pacing activity, and lying down during strong cramps can help. If severe pain continues despite medication, seek medical evaluation. Keeping a simple log of bleeding and pain is useful to share with a clinician if needed.
Common safe pain-management steps you can try at home include:
- Take OTC NSAIDs as directed to reduce cramping and inflammation.
- Use heat: a warm compress or heating pad on the lower abdomen can ease uterine cramps.
- Rest and pace activity: avoid strenuous exercise until bleeding and pain decrease.
These measures often offer meaningful relief and support recovery; contact a clinician if symptoms worsen.
What hygiene and activity guidelines should you follow after abortion?
Keep the vulvar area clean with gentle washing, avoid baths, swimming pools, and douching for the recommended time to lower infection risk, and use sanitary pads instead of tampons until advised otherwise. Wait to resume vaginal intercourse until your provider gives the go-ahead — commonly about one to two weeks — so the cervix can close and infection risk falls; when you do resume sex, use effective contraception if you want to avoid pregnancy. Return to exercise gradually: begin with light walks and increase activity as bleeding and pain permit, listening to your body to avoid pushing too soon. Book any recommended follow-up visits to confirm recovery and discuss contraception or other questions.
If you want extra guidance tailored to recovery and emotional support, Her Smart Choice offers clear, compassionate resources focused on post-abortion care. Their materials can help you plan follow-up, learn self-care steps, and find counseling referrals.
What are the signs of complications after an abortion and when should you seek help?
Knowing warning signs helps you act fast if infection, incomplete abortion, or dangerous bleeding occurs. Emergency red flags include fever over 100.4°F (38°C), foul-smelling vaginal discharge, severe or worsening lower abdominal pain not eased by medication, passing large tissue fragments with heavy bleeding, dizziness or fainting, and soaking through sanitary pads quickly. If you have any of these signs, get urgent medical evaluation or go to emergency care so complications can be treated. Clear thresholds and quick action reduce risk and speed safer recovery.
How can you recognize signs of infection or incomplete abortion?
Infection often shows as fever, chills, increasing abdominal pain, and a foul or unusual vaginal discharge — symptoms that typically get worse rather than better and may come with a general feeling of being unwell or a fast heart rate. Incomplete abortion may present as ongoing heavy bleeding, continued severe cramping beyond the expected timeframe, passage of tissue after the procedure, or rising hCG levels if tested. Comparing the expected pattern (gradual improvement) to warning signs (worsening or new systemic symptoms) helps you decide whether to seek clinical care. If infection or retained tissue is suspected, prompt evaluation and treatment are important to prevent complications.
Short-Term Physical and Psychological Sequelae of Abortion Background: Abortion can be associated with short-term physical and psychological consequences. This study examined those effects across different types of induced abortion in women attending medical centers in Shiraz, Iran. Methods: A cross-sectional sample included 437 pregnancies that ended in abortion, gathered from a larger group of deliveries during a 4-month period. Participants completed demographic questionnaires and the Mississippi Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder Scale (M-PTSD); results were analyzed using standard statistical methods. Short-term physical and psychological health consequences of induced and spontaneous abortion: a cross-sectional study., N Tayebi, 2021
Watch for these infection or incomplete-abortion signals:
- Fever or chills: a sign of systemic infection that needs medical review.
- Foul-smelling discharge: suggests infection and warrants prompt care.
- Persistent or worsening pain: especially if not relieved by medications.
If you notice any of these, contact a healthcare provider for evaluation.
When is heavy bleeding an emergency after abortion?
Heavy bleeding is an emergency when it causes dizziness, fainting, or when you are soaking through more than two sanitary pads per hour for two consecutive hours. Passing large clots (about the size of a lemon or bigger) along with lightheadedness, weakness, or a racing heart also calls for immediate medical attention. If heavy bleeding happens, lie down and, if possible, elevate your feet, call emergency services or go to urgent care, and bring someone with you if you can. After stabilization, clinicians will check for retained tissue, uterine atony, or other causes and arrange treatment that may include medication or procedures.
How does abortion affect fertility and future pregnancy planning?
Most people do not experience long-term infertility after an abortion. Fertility often returns quickly because ovulation may resume within weeks, so pregnancy is possible before your first post-abortion period. Many people get their next period around 4–6 weeks, though timing varies with prior cycle regularity, the abortion method, breastfeeding, and individual hormone recovery. If you want to avoid pregnancy, planning contraception right after the procedure is important since fertility can return fast; many methods can be started immediately depending on local guidance. If you plan to try for pregnancy later, waiting until you feel physically and emotionally ready — and confirming recovery with a clinician if advised — supports healthier planning.
Below is a concise comparison of common contraceptive options, suggested start timing after abortion, and key points to consider when choosing.
| Contraceptive Option | When to Start Post-Abortion | Notes / Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| Combined oral contraceptive pill | Often can start immediately | Requires adherence; may increase bleeding initially |
| Progestin-only pill / injection | Can often start immediately | Good option if estrogen is contraindicated |
| Intrauterine device (IUD) | May be inserted at procedure or after confirmation | Offers long-term protection; immediate-start IUDs available in some settings |
| Implant | Can often start immediately | Highly effective, long-acting option |
| Condoms | Use immediately | Protects against pregnancy and STIs; user-dependent |
This table makes it easier to compare options and choose what fits your needs; individualized counseling is helpful to match a method to your medical history and preferences. For guidance on choosing contraception or planning your next pregnancy, Her Smart Choice provides empathetic, plain-language resources to help you make an informed decision.
When does your menstrual cycle return after abortion?
Your period usually returns in about 4–6 weeks after an abortion for many people, but timing varies depending on how quickly ovulation resumes and how your hormones recover. Factors that affect return include previous cycle regularity, the abortion method, breastfeeding, and individual hormone patterns; some people get their next period sooner, others later. Tracking changes like shifts in cervical mucus, basal body temperature, or bleeding patterns can help you know what to expect after your abortion and inform contraception or pregnancy planning. If your period is much later than expected, check with a clinician for evaluation and reassurance.
What birth control options are recommended post-abortion?
Choosing contraception after abortion depends on personal preferences, medical history, and whether you want immediate protection. Many methods can be started right away to prevent a rapid return to fertility. Long-acting reversible options like IUDs and implants offer highly effective, low-maintenance protection and may be placed at the time of the procedure in some clinics. Pills, injections, and condoms are also valid immediate options depending on your needs. Discussing pros and cons — including side effects, reversibility, and how easy each method is to use — with a clinician or support resource helps you pick the best fit and start protection when you’re ready.
These steps help you get timely, effective pregnancy prevention that matches your preferences and health needs.
Frequently Asked Questions
If severe pain doesn’t respond to over-the-counter pain medicines, seek medical attention. Intense pain can indicate complications such as infection or retained tissue. Monitor your symptoms closely; if pain gets worse or comes with fever or heavy bleeding, contact your healthcare provider right away for evaluation and possible treatment.
Emotional recovery combines self-care, social support, and professional help when needed. Try relaxation practices like mindfulness or journaling, and talk with trusted friends or family about what you’re feeling. If emotions become hard to manage, consider counseling or a support group. Remind yourself that a wide range of feelings is normal, and taking time to process them is an important part of healing.
A balanced diet supports recovery. Eat nutrient-rich foods — fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins — to help your body replenish. Stay hydrated, especially if you experience bleeding. Iron-rich foods (for example, spinach and legumes) may help with fatigue related to blood loss. For personalized guidance, check with your healthcare provider.
Most providers advise waiting about one to two weeks before resuming vaginal intercourse to reduce infection risk and allow the cervix to close; follow the specific guidance from your clinician. When you do have sex again, consider contraception if you want to prevent pregnancy, since fertility can return quickly.
Contact a provider if you develop fever over 100.4°F (38°C), foul-smelling vaginal discharge, severe abdominal pain that worsens, or heavy bleeding that soaks through more than two sanitary pads in an hour for two consecutive hours. These symptoms may signal complications that need prompt evaluation and treatment.
Keep a simple journal of symptoms — note bleeding patterns, pain levels, and emotional changes. Record anything that feels unusual and bring those notes to follow-up visits. Tracking your menstrual cycle also helps you know when to expect your next period and assess overall reproductive health.
Resources include counseling services, support groups, and informational sites like Her Smart Choice. These can offer emotional support, practical advice, and referrals to care. Connecting with others who’ve had similar experiences can also be helpful. Don’t hesitate to reach out if you need support — you don’t have to go through recovery alone.
Follow Us!
Conclusion
Knowing what to expect physically and emotionally after an abortion helps you manage recovery with greater confidence. By recognizing common symptoms, understanding hormonal changes, and using practical self-care strategies, most people navigate this period safely. For personalized support and clear resources tailored to your recovery, consider exploring Her Smart Choice’s guides and services. When you’re ready, reach out for the information and support that fit your needs.