When Do Birth Control Pills Start Working: How Long Until They Protect You?
This guide helps you understand exactly when oral contraceptives begin protecting against pregnancy and gives clear, actionable steps so you can use them with confidence. You’ll get straightforward timelines for combined oral contraceptives (COCs) and progestin-only pills (POPs or “mini‑pills”), learn the biological reasons the timelines differ, and find precise rules for common start methods (Day 1, Quick Start, Sunday Start). The article also walks through missed‑pill actions, when to use backup contraception, and special situations such as postpartum use or starting after an abortion. The practical takeaways are simple: types of birth control methods usually give immediate protection; non‑Day 1 COCs generally need about 7 days of backup; non‑Day 1 POPs generally need about 48 hours.
Follow Us!
How Long Does It Take for Birth Control Pills to Start Working?

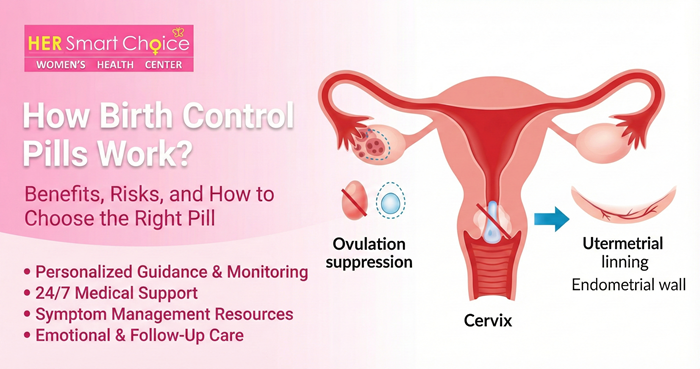
Here’s a concise summary of when pills become effective and why that timing matters. Combined pills mainly prevent pregnancy by stopping ovulation and changing cervical mucus so sperm can’t reach an egg. Progestin‑only pills mostly thicken cervical mucus and sometimes suppress ovulation, which makes precise timing and daily consistency more important. Practically speaking, starting a combined pill on Day 1 of your period usually gives protection right away because ovulation for that cycle is already unlikely. If you start a combined pill at another point, you’ll usually need a short waiting period while ovulation suppression kicks in. For most POPs, a Day 1 start also gives immediate coverage, but starting at other times commonly requires about 48 hours of backup while mucus changes take effect. Knowing how each method works will help you pick the right start and use backup correctly when needed.
This article exists to explain when pills start working and to give clear, evidence‑informed steps so you can manage contraception confidently.
Different start scenarios change how quickly protection begins. The table below gives quick rules and backup recommendations so you can see the most common situations at a glance.
| Pill Type / Start Scenario | Start Method | Time to Effective Protection | Backup Needed (Yes/No & Duration) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Combined pill — Day 1 start | Day 1 of period | Immediate protection (same cycle) | No backup needed if correctly started on Day 1 |
| Combined pill — Quick/Sunday start | Quick Start or Sunday Start | Protection after about 7 days | Yes — use backup for 7 days |
| Progestin-only pill — Day 1 start | Day 1 of period | Immediate protection | No backup needed if correctly started on Day 1 |
| Progestin-only pill — Other start | Quick Start or other | Protection after ~48 hours (2 days) | Yes — use backup for 2 days |
The short rules to remember: Day 1 starts give immediate coverage; combined pills started at other times generally need about seven days; progestin‑only pills started at other times generally need about two days. The next section explains each start method in more detail to help you choose the right approach for your situation.
When Is the Combined Birth Control Pill Effective After Starting?
Combined oral contraceptives prevent pregnancy mainly by stopping ovulation and by changing cervical mucus. If you start a combined pill on the first day of your period (Day 1), most guidance treats you as protected immediately because the hormones align with that cycle’s natural timing. If you begin a combined pill at another point in your cycle (Quick Start or Sunday Start), it typically takes roughly seven days for ovulation suppression and mucus changes to fully reduce pregnancy risk, so use backup during that time. Keep in mind that vomiting, severe diarrhea, or medications that interact with the pill can lower absorption and may extend the time you need backup — in those cases check with your clinician or follow the manufacturer’s instructions.
How Quickly Does the Mini Pill Become Effective?
Progestin‑only pills (POPs) work mainly by thickening cervical mucus and depend heavily on strict daily timing. When taken on Day 1 of bleeding, most POPs provide immediate protection for that cycle because ovulation is unlikely and mucus changes set in quickly. If you start a POP on another day, plan to use backup contraception for about 48 hours while the mucus response becomes reliable. POP effectiveness also depends on taking the pill at the same time every day — some formulations have a narrow window (often around three hours); doses taken outside that window may count as missed and require immediate backup. The next section breaks down start methods and backup requirements step by step.
Progestin-Only Pills (POPs): Safety, Efficacy, and Adherence Considerations Progestin‑only pills are commonly recommended for people who can’t take estrogen (for example, while breastfeeding or with certain health conditions). They have a wide safety profile and are effective when taken correctly, which is why some experts have supported wider access without a prescription. Because POPs rely on precise daily dosing, users need clear guidance about missed or delayed pills; unlike for combined pills, we have less data showing brief nonadherence is harmless with low‑dose POPs. Source: protocol and research summaries on POP adherence and effectiveness (M. Creinin et al., 2021).
What Are the Different Start Methods for Birth Control Pills and Their Effectiveness?

The start method you choose affects how quickly you’re protected and how convenient the schedule is. The three common approaches are Day 1 start, Quick Start, and Sunday Start. Day 1 starts usually give immediate protection for both combined pills and POPs because they coincide with the natural menstrual cycle. Quick Start lets you begin right away on the day you get the pills, which avoids waiting for your next period but generally requires short‑term backup (7 days for combined pills, 2 days for POPs). Sunday Start is chosen for convenience so reminders fall on a consistent weekday; its backup rules match Quick Start and depend on pill type. The table below summarizes procedures, benefits, and when backup is needed.
| Start Method | Typical Procedure | Pros | When Backup Is Required |
|---|---|---|---|
| Day 1 start | Begin on the first day of menstrual bleeding | Immediate protection for most pill types; straightforward rules | Generally not required if correctly started on Day 1 |
| Quick Start | Begin immediately on the day you receive the pill | Fast initiation; avoids waiting | COC: 7 days; POP: 2 days |
| Sunday Start | Begin on the first Sunday after your period begins or when prescribed | Matches weekly routine for easier reminders | COC: 7 days; POP: 2 days |
Choosing the right start method depends on how quickly you need protection and what fits your routine. The following section lists the main reasons to use backup contraception and exactly how long to use it, so you can act with confidence if circumstances change.
How Does Starting on Day 1 of Your Period Affect Effectiveness?
Starting on Day 1 lines up the pill’s hormones with your cycle, lowering the chance of ovulation that cycle and typically giving immediate contraceptive protection. Since ovulation usually happens mid‑cycle, beginning on the first day of bleeding prevents the later steps required for pregnancy in that cycle. Exceptions include the postpartum period, breastfeeding, or when you’re taking interacting medications — in those situations a clinician may recommend different timing or temporary backup. For most people, Day 1 is the simplest way to avoid a waiting period and begin protection right away.
What Is the Quick Start and Sunday Start Method, and When Is Backup Needed?
Quick Start means you start the pill the day you get it instead of waiting for your period; Sunday Start means you begin on the first Sunday after your chosen start date. Both are convenient and can improve adherence, but they usually require short‑term backup because protection takes a few days to build. For combined pills, use condoms or avoid sex for seven days after starting with Quick or Sunday Start; for progestin‑only pills, use backup for two days. If you’ve had recent unprotected sex or suspect pregnancy, consider testing or clinical advice before Quick Start. These start options let you begin on your schedule while staying protected with the recommended backup rules.
When and Why Do You Need Backup Contraception with Birth Control Pills?
Use backup contraception whenever your pill protection is uncertain or temporarily interrupted — for example, after non‑Day 1 starts, missed or late pills, drug interactions, or vomiting/diarrhea. Pills rely on steady hormones and mucus changes; anything that disrupts hormone levels or timing can create a window when pregnancy is possible. A simple rule of thumb helps decision‑making: for combined pills use backup for seven days after a late start or multiple missed pills; for progestin‑only pills use backup for 48 hours in comparable situations. Backup options include condoms or abstinence; emergency contraception is a separate option if you had unprotected sex during a high‑risk window. The lists below show common scenarios that require backup and what to do right away.
- Common situations that require backup contraception:Starting pills not on Day 1 (Quick/Sunday starts) Missing one or more pills or taking pills late beyond the allowed window Vomiting or severe diarrhea within a few hours of taking a pill Taking medications that interact and reduce contraceptive effectiveness
- Immediate actions to take when backup is needed:Use condoms or avoid sex until the backup period ends Keep taking your pills as directed (don’t skip more doses) Consider emergency contraception if you had recent unprotected sex Contact a clinician if you missed multiple pills or are on interacting medications
How Long Should Backup Contraception Be Used for Combined Pills?
For combined oral contraceptives, the standard waiting period after a non‑Day 1 start or after missed pills is seven days. This gives the hormones time to reliably suppress ovulation and establish protective mucus changes. If you miss a single combined pill but take it within about 24 hours, you’ll usually maintain protection; missing multiple pills or having longer gaps typically triggers the seven‑day backup rule and may prompt consideration of emergency contraception if you had unprotected sex. Helpful prevention tips include setting daily reminders, using a pill organizer, and using condoms during the seven‑day backup window. If vomiting, interactions, or many missed doses occur, check with your clinician.
How Long Is Backup Needed for the Mini Pill?
For progestin‑only pills, backup is usually required for 48 hours (two days) after a non‑Day 1 start or after a missed or late dose that falls outside the pill’s allowed timing window. POPs rely on consistent hormone levels and mucus thickness, so even brief delays can reduce effectiveness — hence the shorter but strict backup interval. If you miss a POP dose beyond its allowed window, take the missed pill as soon as you remember and use condoms or avoid sex for 48 hours. Simple strategies like phone alarms, carrying extra packs, and tying pill time to a daily habit help avoid lapses that would trigger the backup rule.
What Should You Do If You Miss a Birth Control Pill?
Knowing pill‑type specific steps helps reduce pregnancy risk and tells you when to use backup or seek emergency contraception. The main difference is between combined pills and progestin‑only pills: combined pills often have a longer grace period for one missed dose and different advice for multiple misses; POPs have a very narrow timing window, so many late doses count as missed. Immediate steps include taking the missed pill as soon as you remember, continuing the pack, and starting backup if you’re outside the acceptable window. The table below summarizes common scenarios and the recommended actions so you can act quickly.
| Pill Type | Miss Window | Immediate Steps | Backup / Emergency Contraception Recommendation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Combined (1 missed) | Missed 1 active pill (<24 hours usually) | Take the missed pill ASAP, then continue the pack | Generally no backup if taken within the window; otherwise use backup for 7 days |
| Combined (≥2 missed) | Two or more active missed pills | Take the most recent missed pill immediately, discard others if instructed, continue the pack | Use backup for 7 days; consider emergency contraception if you had unprotected sex |
| Progestin-only (missed timing) | Dose taken outside allowed time window (e.g., >3 hours) | Take the missed pill ASAP, then resume your regular schedule | Use backup for 48 hours; consider emergency contraception if you had unprotected sex |
These steps will help you restore protection quickly. The next sections give simple, stepwise instructions for each pill type so you can follow the right actions under stress.
How to Manage Missed Combined Pills to Maintain Protection?
If you miss a single combined pill and can take it within about 24 hours, take it as soon as you remember and keep taking the rest of the pack — most guidance treats this as maintaining protection. If you miss two or more active combined pills, take the most recent missed pill immediately (discard earlier missed pills if directed), continue the pack, and use backup contraception for seven days. If you had unprotected sex in the days before missing pills, emergency contraception may be appropriate — contact a clinician to discuss timing and options. After an episode of missed pills, consider stronger adherence supports like daily alarms, pill boxes, or apps to help avoid future gaps.
What Are the Guidelines for Missed Mini Pills and Timing Windows?
For progestin‑only pills, a missed dose usually means taking the pill outside the strict daily timing window (commonly about three hours for many POPs). That missed timing can immediately reduce protection. If you miss or take a POP late, take the missed pill as soon as you remember and then use backup contraception for 48 hours while keeping to your daily schedule. If you had unprotected intercourse during the missed window, consider emergency contraception and contact a clinician promptly. Practical prevention strategies — setting a fixed daily time, alarms, and carrying pills when you travel — are very effective at avoiding missed‑dose problems.
How Do Special Situations Affect When Birth Control Pills Start Working?
Certain situations — childbirth and breastfeeding, recent abortion or miscarriage, or switching between pill types — can change recommended start timing and backup needs. After delivery, especially while breastfeeding, clinicians often avoid estrogen‑containing pills at first because estrogen can reduce milk supply; progestin‑only pills or non‑hormonal methods may be preferred early on, and protection timing will follow the specific method’s rules. After abortion or miscarriage, many protocols allow immediate pill start to provide prompt protection, though backup needs depend on timing and method. When switching pills, keep continuity (finish a pack or follow your clinician’s instructions) to avoid gaps; backup might be necessary during the transition. The table below outlines typical rules for these scenarios so you know what to expect.
| Scenario | Typical Rule | Backup Needed |
|---|---|---|
| Postpartum (non-breastfeeding) | May start combined pills after a short interval | Often follows Day 1 or Quick Start rules; backup may be required |
| Breastfeeding | Estrogen-containing pills are often delayed; POPs are preferred | Backup rules depend on timing and clinician advice |
| After abortion/miscarriage | Immediate start is often permitted | Backup may not be needed in some cases; follow clinician guidance |
These scenario‑based rules show why personalized clinical advice matters in special circumstances. The following subsections give practical guidance for postpartum and post‑abortion situations.
When Does Birth Control Become Effective After Childbirth or While Breastfeeding?
Timing after childbirth depends on breastfeeding and your medical history. Because estrogen can reduce milk supply for some people, clinicians often delay estrogen‑containing combined pills while breastfeeding and prefer progestin‑only options early on. If a POP is started immediately after delivery, the usual POP timing rules apply and backup depends on whether it was a Day 1 start. If you are not breastfeeding, combined pills may be started according to local guidance, with Day 1 or Quick Start rules and the usual backup requirements. Because personal health factors and breastfeeding goals affect the best choice, check with your clinician for individualized advice before starting or changing pills after childbirth.
How Does Starting Birth Control After Abortion or Miscarriage Impact Effectiveness?
After an abortion or miscarriage, many protocols allow immediate initiation of oral contraceptives because the uterus is not pregnant and rapid protection is often useful. Whether you need backup depends on the exact timing and the method used: starting on Day 1 of bleeding often gives immediate protection in guidance from some providers, while Quick Start generally requires the standard 7‑day (COC) or 2‑day (POP) backup. Immediate initiation can help prevent another unintended pregnancy and simplify follow‑up care, but confirm there are no contraindications and arrange appropriate follow up. If you’re unsure or had recent unprotected sex, consider pregnancy testing and talk to a clinician about emergency contraception options.
What Are Common Myths and FAQs About Birth Control Pill Effectiveness?
Several myths about pill effectiveness persist. Clear, direct answers help reduce confusion and support correct use. Two frequent concerns are whether pregnancy is possible during the first week after starting pills and whether pills work immediately after you begin. The short answers are: yes, pregnancy is possible in the first week if you didn’t start on Day 1 and didn’t use backup; and no, pills are not always effective immediately unless started on Day 1 — non‑Day 1 COCs generally need seven days and POPs generally need two days of backup. Below are quick myth‑busting points and a small FAQ that cover the most practical questions people ask.
- Can you get pregnant during the first week of birth control? Yes — if you did not start on Day 1 and did not use backup, the first week can carry risk, especially with Quick or Sunday Starts.
- Does missing one pill always cause pregnancy? No — a single missed combined pill taken within the allowed window usually preserves most protection, but multiple missed pills increase risk and typically require backup.
- Do stomach bugs make pills ineffective? Vomiting or severe diarrhea within a few hours of taking a pill can reduce absorption; treat the dose as missed and follow backup guidance.
- Can other medicines stop my pill from working? Some medicines and supplements interact with hormonal contraception and can reduce effectiveness; check with a clinician or pharmacist when starting new drugs.
These quick answers address common concerns; the final subsections give concise responses to two widely searched questions to support clarity and practical decision making.
Can You Get Pregnant During the First Week of Birth Control?
Yes — pregnancy is possible during the first week if you didn’t start on Day 1 and didn’t use backup during a Quick or Sunday Start. The actual risk depends on where you are in your cycle and whether you had recent unprotected sex, because ovulation can occur before the pill’s full protective effects are established. If you began with a non‑Day 1 start and had unprotected intercourse, consider emergency contraception depending on timing, and use backup contraception for the recommended seven days for COCs or two days for POPs.
Does Birth Control Work Immediately After Starting?
Birth control pills work immediately only when started on Day 1 of bleeding for most protocols. Otherwise, you must wait the standard protection window — about seven days for combined pills and about two days for progestin‑only pills. The Day 1 rule applies because it aligns with the natural cycle and lowers the chance of ovulation that cycle. With Quick Start or Sunday Start, use backup for the specified period until hormonal and mucus‑based protection is established.
Frequently Asked Questions
If you miss two or more active combined pills, take the most recent missed pill as soon as you remember and discard any earlier missed pills if directed. Continue taking the rest of the pack on schedule, but use backup contraception for the next seven days. If you had unprotected sex in the days before the missed pills, talk with a healthcare provider about emergency contraception options.
Yes — you can switch pill types, but do it in a way that avoids gaps in protection. Follow your clinician’s instructions or the manufacturer’s guidance: either finish your current pack or begin the new pill as recommended. Backup contraception may be needed during the transition if there’s any gap. When in doubt, consult your healthcare provider for personalized advice.
Most common antibiotics do not reduce pill effectiveness, but there are exceptions — rifampin and similar medications can interfere with hormonal contraception. If you’re prescribed antibiotics that may affect the pill, use backup contraception during treatment and for at least seven days after finishing, or follow your provider’s guidance. Always check with your clinician or pharmacist about specific interactions.
Possible signs include unexpected bleeding or spotting, missed periods, or symptoms of pregnancy such as nausea or breast tenderness. If you notice these signs, especially after unprotected sex, take a pregnancy test and contact your healthcare provider. Also review your pill‑taking routine to make sure you’re taking pills on schedule.
Many people safely use pills continuously to skip periods or reduce symptoms, and some formulations are designed for continuous use. Continuous use may be recommended for specific medical reasons, but it’s best to discuss this with your provider to confirm it’s appropriate for you and to choose the right regimen.
If you have side effects such as nausea, headaches, or mood changes, talk with your healthcare provider. They can help determine whether side effects are likely to settle or whether switching to a different formulation or method would be a better option. Don’t stop taking your pills without medical advice unless directed to do so.
Conclusion
Knowing when birth control pills start protecting you makes it easier to use them correctly and confidently. Remember the simple timelines: Day 1 starts usually give immediate protection; combined pills started at other times typically need about seven days of backup; and progestin‑only pills started at other times typically need about 48 hours. Choosing the right start method, sticking to a daily routine, and using backup when needed will keep you protected. If you have special circumstances or are unsure, check with your healthcare provider for personalized guidance and explore our resources for more tips on managing your contraception.
Follow Us!