How Accurate Are Pregnancy Tests? Understanding Accuracy, Causes, and Best Practices
Home pregnancy tests deliver remarkable pregnancy test accuracy by detecting human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) levels with up to 99 percent reliability after a missed period. This guide explains how detection thresholds, timing, user technique and test design interact to influence result confidence. Readers will learn which factors affect accuracy, why false positives and negatives occur, which test types offer the greatest reliability, the ideal testing window and how ovulation testing can inform pregnancy detection. By mastering these insights, individuals can improve result clarity and select appropriate testing resources from Her Smart Choice’s trusted test kits and expert guidance.
Follow Us!
What Factors Affect Pregnancy Test Accuracy?
Pregnancy test accuracy depends on how effectively a test detects hCG hormone, the timing of testing relative to implantation, the sensitivity threshold of the assay and proper user technique to ensure reliable outcomes. Understanding these components supports timely confirmation of pregnancy and minimises misinterpretation. For example, choosing a high-sensitivity strip and testing first morning urine can enhance detection soon after implantation and prevent inconclusive results.
What Role Does hCG Play in Pregnancy Test Accuracy?
Home pregnancy tests detect human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) hormone produced by the placenta after implantation, and rising hCG concentrations directly influence test sensitivity and result validity. hCG doubles every 48–72 hours in early pregnancy, and tests calibrated to detect as low as 10–25 mIU/mL can signal pregnancy before a missed period. Monitoring these hormone levels underpins reliable early detection and guides healthcare consultation when levels vary unexpectedly.
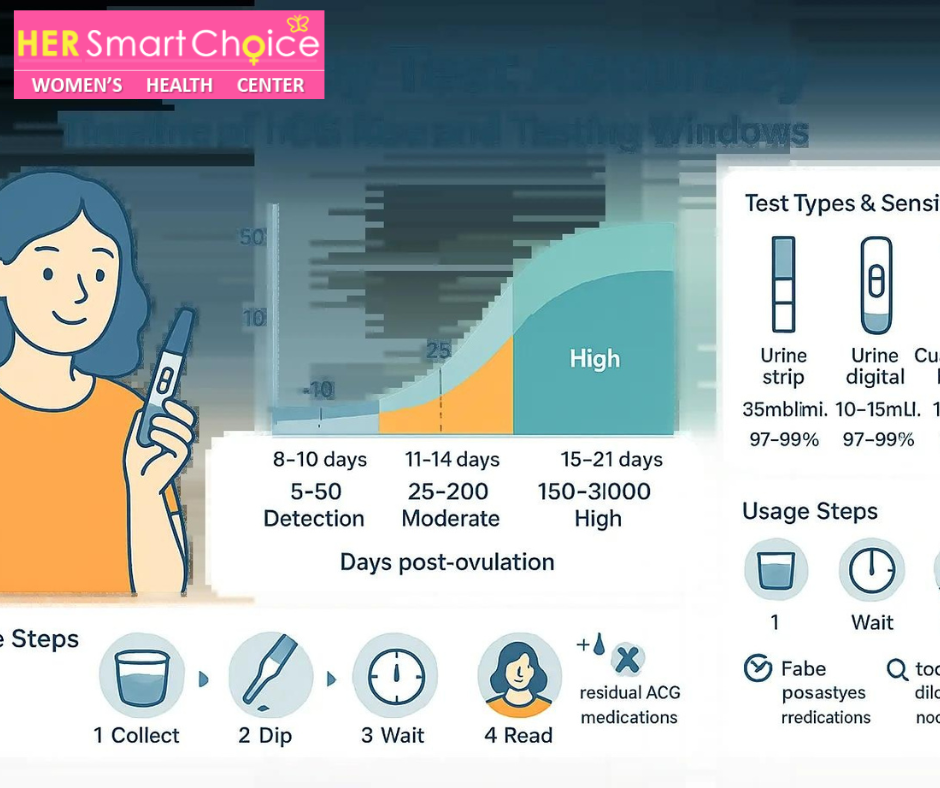
How Does Timing Impact Pregnancy Test Accuracy by Day?
Optimal timing critically improves pregnancy test reliability because hCG levels must exceed the test’s detection threshold for a positive result. Testing too soon after ovulation often yields negative or faint results, whereas waiting until at least the first day of a missed period raises accuracy above 97 percent. Planning test timing based on cycle tracking and ovulation analysis ensures the hormone concentration reaches detectable levels for consistent outcomes.
How Does Test Sensitivity Influence Accuracy?
Test sensitivity describes the lowest hCG concentration a device can reliably detect, typically ranging from 10 to 50 mIU/mL for home kits. Higher-sensitivity tests (10–15 mIU/mL) enable earlier detection before a missed period, while standard sensitivity (25 mIU/mL) suits testing after expected menstruation. Selecting tests with appropriate sensitivity levels improves early confirmation capability and reduces the chance of false negatives.
What User Errors Can Affect Pregnancy Test Results?
User errors such as reading results outside the recommended time window, using expired kits, insufficient urine volume or misinterpreting evaporation lines can undermine accuracy. Skipping instructions on timing and ignoring humidity warnings may produce misleading faint lines or false positives. Careful adherence to manufacturer guidelines, checking expiration dates and following timing windows preserves test reliability.
How Do Different Types of Pregnancy Tests Compare in Accuracy?
Pregnancy tests fall into urine-based at-home strips, digital displays and clinical blood assays, each offering distinct sensitivity and accuracy profiles. Comparing these options reveals trade-offs between early detection, ease of use and confirmation certainty. Understanding these differences helps individuals choose the right test for their needs and improves confidence in the result.
| Test Type | Sensitivity (mIU/mL) | Typical Accuracy (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Urine (Home Strip) | 25 | 97–99 |
| Urine (Digital) | 10–25 | 97–99 |
| Blood (Quantitative) | 1–5 | 100 |
Higher-sensitivity blood assays guarantee detection but require clinical sampling, whereas home urine tests balance convenience and accuracy. Recognising these distinctions informs timing and test selection.
What Causes False Positive Pregnancy Test Results?

A false positive occurs when a test indicates pregnancy in the absence of an ongoing gestation, driven by residual hCG, certain medications, medical conditions or misreading evaporation artifacts. Identifying these causes prevents unwarranted stress and guides follow-up decisions.
How Can Chemical Pregnancies Lead to False Positives?
Chemical pregnancies represent very early miscarriages after implantation, where hCG briefly rises and triggers a positive result before levels fall. Individuals may observe a faint positive line that disappears within days, reflecting transient hormone p1roduction rather than a viable pregnancy. Distinguishing this pattern requires retesting and healthcare evaluation.
Which Medications Can Cause False Positive Results?
Medications containing hCG, such as fertility injections or some hormone therapies, can maintain elevated hormone levels and yield positive tests even when pregnancy is not present. Recognising recent fertility treatment use clarifies test interpretation and avoids confusion over persistent hCG from exogenous sources.
What Medical Conditions May Result in False Positives?
Rare conditions like ovarian cysts, trophoblastic disease or certain tumours can secrete hCG and trigger a positive test. Persistent positive readings despite negative clinical evaluations warrant medical investigation to rule out underlying pathology and confirm pregnancy status.
How to Distinguish Evaporation Lines from True Positive Results?
Evaporation lines appear as faint, colourless streaks once urine dries, whereas true positives manifest a coloured line within the specified reading window. Reading results within the manufacturer’s time frame, comparing control and test line hues and consulting instructions ensure genuine positives are correctly identified before concluding a false positive scenario.
What Are the Common Causes of False Negative Pregnancy Tests?
False negatives occur when a test fails to detect hCG in a pregnant individual, often due to insufficient hormone levels, diluted urine, incorrect usage or rare antibody interference. Recognising these factors guides retesting and timing adjustments.
Why Does Testing Too Early Cause False Negatives?
Testing before hCG rises above the detection threshold yields negative results despite implantation, since hormone levels may remain below 25 mIU/mL in the first week after conception. Waiting until at least the day of a missed period increases test sensitivity and reduces false negative risk by ensuring adequate hormone concentration.
How Does Diluted Urine Affect Pregnancy Test Accuracy?
Drinking excessive fluids prior to testing dilutes hCG concentration in urine, potentially dropping levels below the test’s sensitivity threshold and causing a negative result. First morning urine typically offers the highest hormone concentration for accurate detection and avoids dilution-related false negatives.
What Is the Hook Effect and How Does It Cause False Negatives?
The hook effect arises when extremely high hCG concentrations overwhelm test antibodies, preventing proper sandwich formation and leading to a negative or weak positive result. This rare phenomenon can occur in molar pregnancies or late first trimester tests, prompting dilution of the sample and retesting to obtain accurate results.
The hook effect, a phenomenon where extremely high hCG levels can lead to false negative results, has been documented in various studies.
The Hook Effect in Pregnancy Testing and Dilution Methods … It can be overcome by dilution of the test sample if suspicion is high.(8) The hook effect may confound pregnancy test results for patients who undergo the test several weeks after …Molar pregnancy with false negative urine hCG: the hook effect, H Rajesh, 2010
This effect can be overcome by diluting the test sample if suspicion is high, and it may confound pregnancy test results for patients who undergo the test several weeks after conception.
Further research has explored the implications of the hook effect, particularly in cases of complete molar pregnancy.
False Negative Pregnancy Tests Resulting from the Hook Effect … resulting in a false negative test result. The hook effect is not limited to β-hCG testing and … As a less prevalent disease, a two-step process for all β-hCG samples will add …False Negative Urine Pregnancy Testing with Complete Molar Pregnancy: An Example of the Hook Effect., M Khan, 2016
This phenomenon is not limited to β-hCG testing and can lead to false negative results in specific clinical scenarios.
Can Ectopic Pregnancy Lead to False Negative Results?
Ectopic pregnancies may produce lower-than-expected hCG levels that rise slowly, causing some tests to read negative despite implantation outside the uterus. Persisting pregnancy symptoms with negative tests should prompt medical evaluation for ectopic implantation and follow-up blood hCG monitoring.
What Should You Do After a False Negative Pregnancy Test?
After a negative test with ongoing pregnancy signs, individuals should wait 48–72 hours and retest using first morning urine or choose a more sensitive assay. Consulting a healthcare professional for a quantitative blood test can confirm pregnancy status and rule out conditions like ectopic gestation.
Which Types of Pregnancy Tests Are Most Reliable?
Reliability depends on the test method, sensitivity threshold and sample type, with blood assays offering definitive confirmation and digital home tests combining ease of reading with high sensitivity. Evaluating each option’s strengths ensures informed selection for personal circumstances.
How Accurate Are Urine Pregnancy Tests at Home and in Clinics?
Home urine tests typically achieve 97–99 percent accuracy after a missed period, while clinic-administered urine assays with professional interpretation can approach similar rates. Both rely on comparable immunoassay technologies, but professional administration reduces user error and misinterpretation.
Why Are Blood Pregnancy Tests Considered More Accurate?
Blood pregnancy tests measure quantitative hCG levels down to 1–5 mIU/mL, delivering 100 percent accuracy in detecting pregnancy earlier than urine tests. Quantitative assays track hormone progression and guide clinical decisions, whereas qualitative urine tests only indicate presence above a fixed threshold.
Are Digital Pregnancy Tests More Accurate Than Traditional Tests?
Digital pregnancy tests offer the same immunoassay accuracy as traditional strip tests but display clear “pregnant”/“not pregnant” readouts, reducing misinterpretation of faint lines. Although sensitivity remains comparable, digital displays enhance user confidence and minimise reading errors.
What Are Early Detection Pregnancy Tests and How Reliable Are They?
Early detection tests use heightened sensitivity (10–15 mIU/mL) to identify hCG several days before a missed period, delivering accuracy rates of 76–93 percent when used four to six days early. Confirmatory testing on or after the expected period improves reliability to above 97 percent.
When Is the Best Time to Take a Pregnancy Test for Maximum Accuracy?
Selecting the optimal testing window increases hormone concentration above sensitivity thresholds and improves detection consistency. Timing testing around cycle events and sample quality ensures definitive results.
Why Is First Morning Urine Recommended for Testing?
First morning urine contains the highest hCG concentration after overnight accumulation, improving detection in early pregnancy and reducing false negatives. Using this sample elevates hormone levels above sensitivity thresholds, especially when hCG rise is still modest.
How Long After Ovulation or Missed Period Should You Test?
Waiting at least 10–14 days post-ovulation or the first day of a missed period allows hCG to exceed 25 mIU/mL, raising accuracy above 97 percent. Testing earlier with high-sensitivity kits is possible but yields lower reliability until hormone levels climb further.
What Is the Step-by-Step Guide to Using a Home Pregnancy Test Correctly?
Follow these steps to maximise accuracy:
- Collect first morning urine in a clean container.
- Dip the test strip for the recommended time.
- Place the strip on a flat surface and wait the specified minutes.
- Read results within the time window, comparing control and test lines.
Proper adherence to each instruction ensures accurate hCG detection and prevents user error from affecting outcomes.
How Should You Interpret Pregnancy Test Results?
A clear control line confirms test validity, and any coloured test line indicates hCG presence above the sensitivity threshold. Absence of a test line denotes a negative result, while faint lines warrant retesting after 48–72 hours or clinical blood testing for confirmation.
How Do Ovulation Tests Relate to Pregnancy Test Accuracy?
Ovulation tests detect luteinising hormone (LH) surges and help predict fertile windows, indirectly supporting optimal timing for pregnancy tests by indicating likely conception dates. Understanding both assays creates a cohesive strategy for fertility tracking and early pregnancy detection.
How Reliable Are Ovulation Tests in Predicting Fertile Windows?
Ovulation tests achieve 80–90 percent reliability in detecting LH peaks when used correctly, guiding intercourse timing for conception. Accurate LH surge identification correlates with impending ovulation and informs planning for pregnancy testing days later.
How Can Ovulation Test Results Help Time Pregnancy Tests?
Identifying the LH surge allows individuals to estimate 10–12 days until hCG levels rise sufficiently for detection, enabling scheduled testing that aligns with expected hormone thresholds. This approach integrates fertility tracking with precise pregnancy confirmation timing.
What Are the Differences Between Ovulation and Pregnancy Test Strips?
Ovulation strips target LH with one set of antibodies and indicate surge timing, whereas pregnancy strips target hCG with a different antibody configuration and sensitivity threshold. Colour changes on ovulation strips mark pre-ovulatory spikes, while pregnancy strips display lines only when hCG rises above detection limits.
What Are Typical hCG Levels During Early Pregnancy and How Do They Affect Test Accuracy?
Typical hCG trajectories guide test selection and timing, as understanding hormone ranges at various stages ensures assays match expected concentrations and minimise inaccurate results.
How Do hCG Levels Change in Early Pregnancy?
hCG levels rise rapidly after implantation, approximately doubling every 48–72 hours until peaking around weeks 8–11. Early concentrations range from 5–50 mIU/mL at 8–10 days post-ovulation and climb to 1,500–200,000 mIU/mL by week 6, enabling progressive detection improvements.
| Days Since Ovulation | hCG Range (mIU/mL) | Detection Likelihood |
|---|---|---|
| 8–10 | 5–50 | Low |
| 11–14 | 25–200 | Moderate |
| 15–21 | 150–3,000 | High |
The accuracy of home pregnancy tests is closely tied to their ability to detect varying levels of human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG), with some studies questioning the reliability of these tests given the variability in hCG concentrations.
Accuracy of Home Pregnancy Tests and hCG Detection Limits Considering our findings regarding human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG), alongside the analytical detection limits of home pregnancy tests and the considerable variability in hCG concentrations, we question the claims of home…Detection of early pregnancy forms of human chorionic gonadotropin by home pregnancy test devices, SA Butler, 2001
This research highlights the importance of understanding the analytical detection limits of home pregnancy tests in relation to the considerable variability in hCG concentrations.
What hCG Levels Are Needed for Different Pregnancy Tests to Detect Pregnancy?
Different assays require specific thresholds:
- Early detection kits: ≥10 mIU/mL
- Standard home tests: ≥25 mIU/mL
- Clinic urine strips: ≥10 mIU/mL
- Quantitative blood tests: ≥1 mIU/mL
Matching test sensitivity to anticipated hCG increments promotes accurate early confirmation.
How Can Variations in hCG Levels Cause Inaccurate Test Results?
Slow-rising hCG in ectopic pregnancies, chemical pregnancies or molar gestations may remain below detection thresholds, leading to false negatives. Conversely, residual hCG from recent pregnancy loss or exogenous hormones can sustain positives independent of viable pregnancy. Recognising these variations directs appropriate retesting and medical evaluation.
A cohesive understanding of hCG dynamics, assay thresholds and timing strategies enhances confidence in pregnancy test accuracy and supports timely healthcare consultation when results deviate from expectations.
Pregnancy test accuracy hinges on aligning assay sensitivity with rising hCG levels, rigorous adherence to testing guidelines and informed interpretation of results. By m==astering hormone detection principles, timing strategies and test selection, individuals can minimise false results and make clear reproductive choices. Her Smart Choice’s range of high-sensitivity strips and digital kits, combined with expert resources, empowers women to navigate early pregnancy confirmation with confidence.
Frequently Asked Questions
You can get pregnant as soon as two weeks after stopping birth control pills, depending on your body’s natural hormone cycle.
Yes. It can take a few weeks to a few months for your period to regulate after stopping birth control.
No. Birth control doesn’t cause infertility. Your fertility usually returns once your hormones balance naturally.
You can try right away, but some doctors recommend waiting until you’ve had one normal menstrual cycle to track ovulation accurately.
If you’ve been trying for 6–12 months without success, consider visiting a fertility specialist for guidance.
Follow Us!
Disclaimer
This article is for educational purposes only and should not replace professional medical advice. Pregnancy test accuracy can vary depending on timing, hormone levels, and test type. For personalized care, please consult with Her Smart Choice or Women’s health clinic near you.